Stay tuned!
Subscribe to the newsletter to stay informed about our new training courses, our new products and our latest tips for growing your truffle farm!
When it comes to managing crop irrigation, measuring the percentage of soil moisture is not enough to give a good estimate of the water reserves available to plants and fungi. Indeed, for the same level of soil moisture, the proportion of water that can be extracted varies enormously depending on the nature of the soil, such as itstexture (levels of clay, silt, sand, porosity) and itsstructure. In a soil, it is therefore necessary to differentiate between :
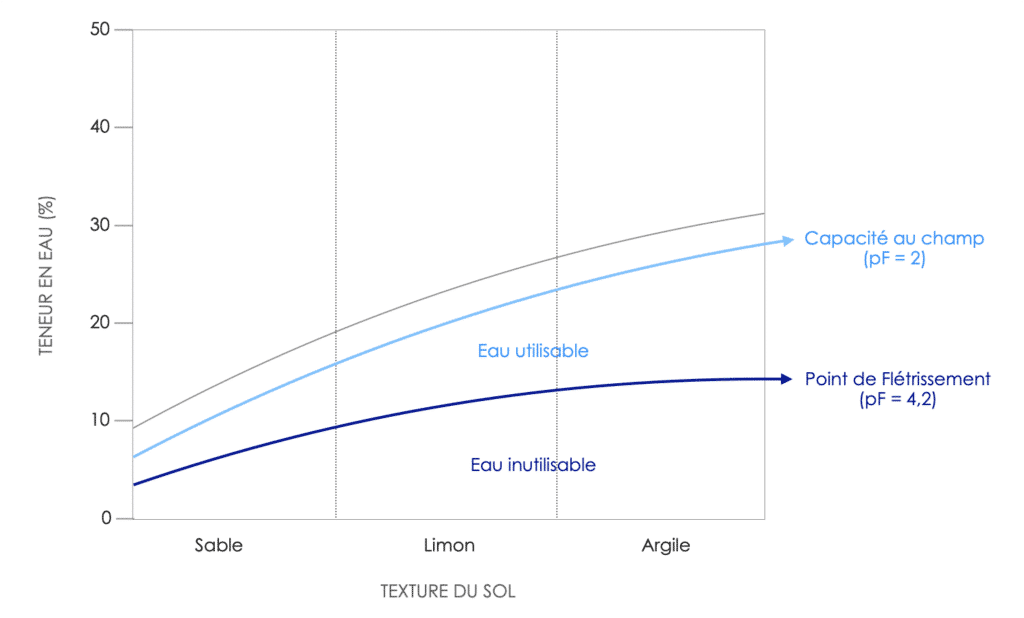
It is therefore essential to assess the proportion of water that can be used for any crop, including truffles. Measuring the pF,the hydrical potentiale, is therefore much better suited to watering management. The pF represents the pressure that needs to be applied to extract the water from the soil. Theoretically, the pF index can reach values between 1 and 6. In practice, however, it is generally observed that for waterlogged soil (” field capacity »), the pF varies between 2 et 2,5. When the usable water reserve decreases, as in the case of drought for example, the value of the water potential increases. When the pF reaches a value of 4-4.2, the water remaining in the soil porosity becomes too difficult for plants and fungi to extract, as the pressure required to do so is too great. The plants then begin to wilt (known as “wilting”). point from wilt » à pF = 4,2). The useful water reserve of a soil is therefore considered to be between pF = 2.5 and 4.2.
Beyond that, the water reserve is unusable. In order to effectively manage the amount of water applied to the field in a controlled and reasoned manner, it is strongly recommended that tools be used to measure in-situ of the pF to a value of 4,2.
The use of sensor is therefore strongly recommended to ensure that water is added in a controlled and reasoned way, as part of an ecological approach to preserving resources.
Based on studies carried out by the IAM(Tree/Micro-organism Interactions) of the INRAE/Université de Lorraine joint research unit WETRUFhas developed a tool for the direct monitoring of pF in the soil: the pF Tracer ®.
This innovation is part of an ecological approach to preserving water resources. This tool was developed following the CulturTruf, coordinated by INRAE, in collaboration with French Federation of Truffle Growersand financed byFranceAgriMer. Implemented since 2016, this project aims to study the effect of cultivation techniques on the biological cycle of the truffle and to observe their impact on the soil’s water regime. Initial results from this project have shown that for black truffles, the threshold value at which irrigation of the truffle bed becomes necessary is pF = 4. Keeping the pF below 4 has enabled truffle growers in the network to achieve normal production despite the various droughts. On the other hand, an experiment using a threshold of pF = 4 as the watering threshold showed a significantly positive impact compared with trees that were not watered. The pF Tracer ® is a simple tool that’s easy to use in the field. It consists of a playback unit specially adapted to gypsum probes.
This innovation, based on a specific calibration, enables pF to be read accurately and directly, without the need for any conversion. It’s easy to install. The sensor are buried in the ground at the foot of the truffle trees. All you have to do is connect the measurement box to it and you can monitor the soil hydric potential.
LICENCE DE SAVOIR-FAIRE INRAE – WETRUF- For the operation and marketing of the tool.
Read our article to find out about the initial feedback from using pF Tracer ®.
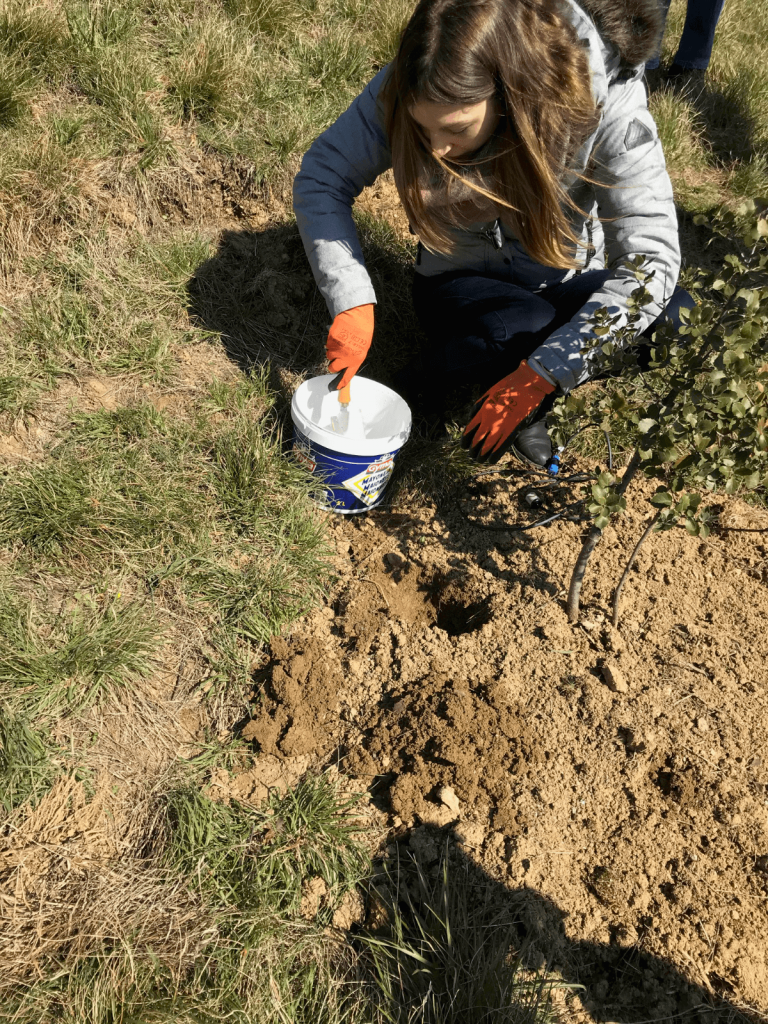
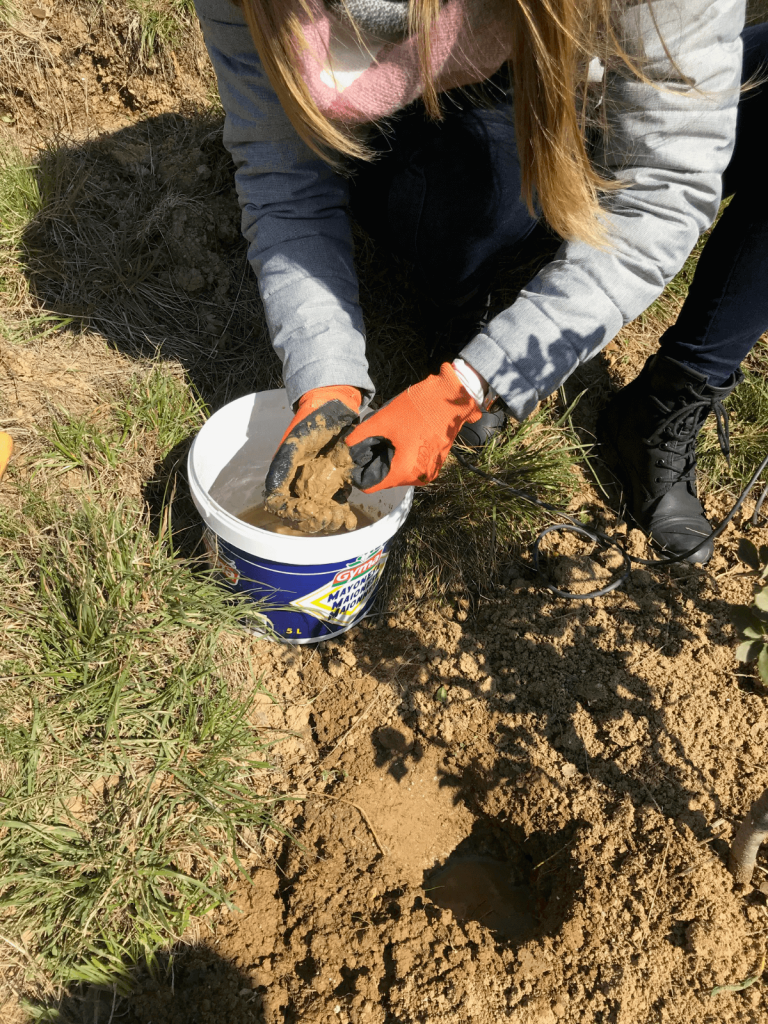
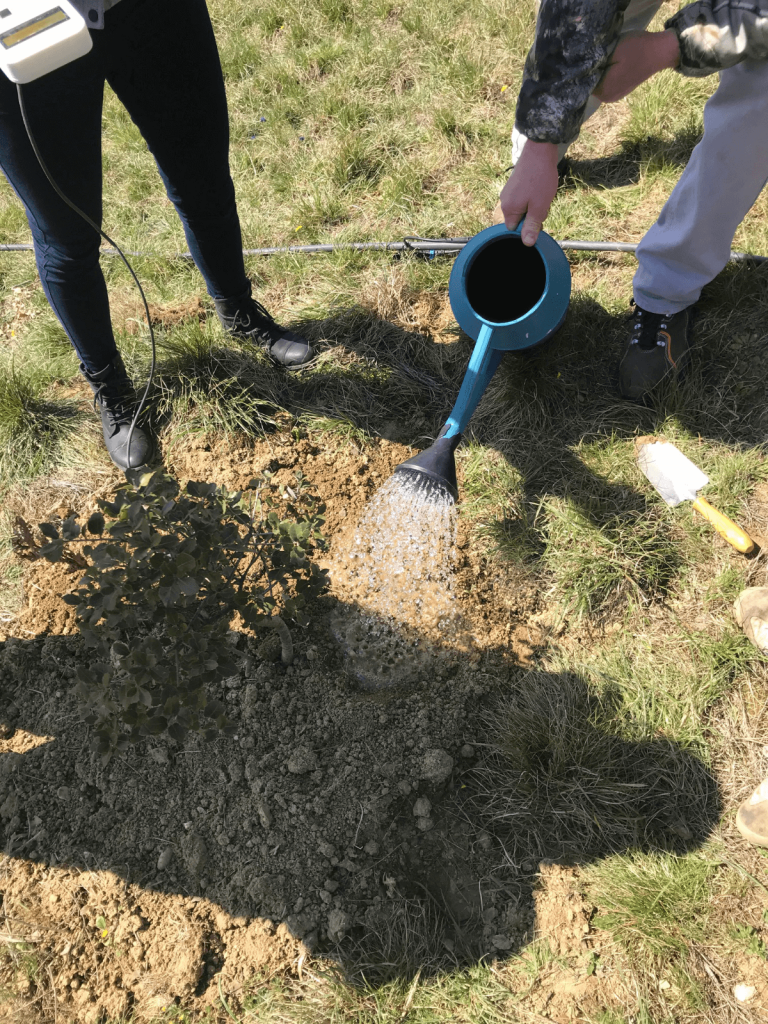
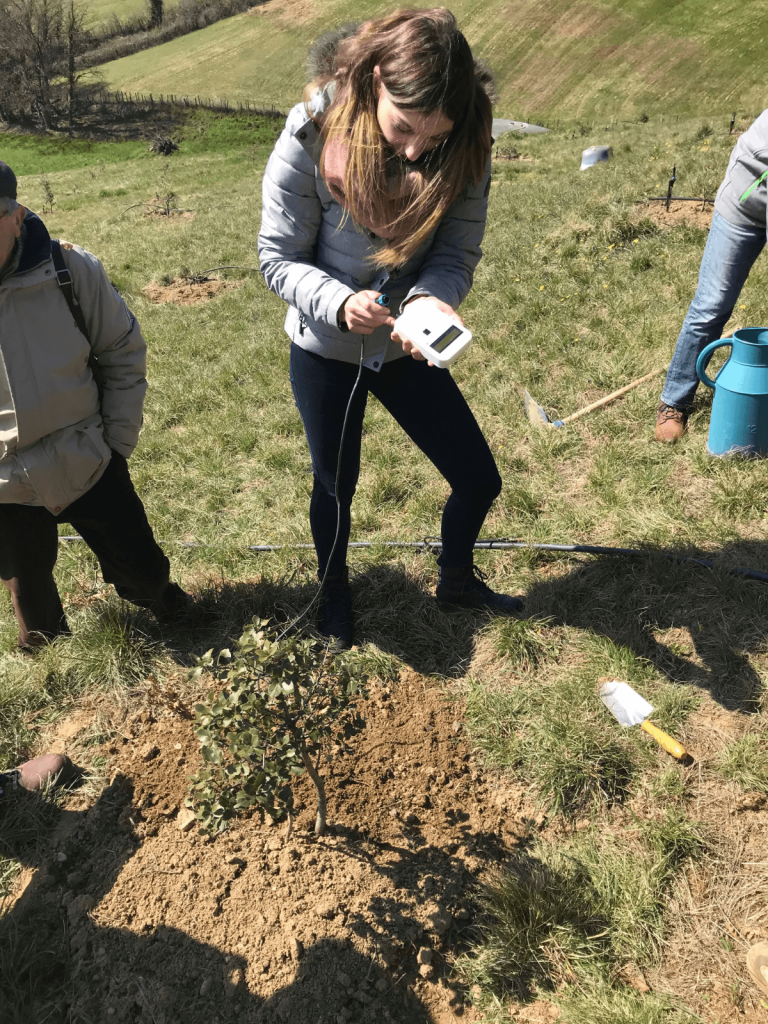




The projectCulturTruf highlights the fact that growing truffles naturally requires less water than other crops. Monitoring the soil hydric potential during dry spells means that we can accurately assess the amount of water needed to water the truffle beds. In this way, truffle production is optimised, while ensuring that watering is rational and controlled. Experiments are continuing within the CulturTruf project to determine watering thresholds for other truffle species, and also to test the use of additional devices (shading, mulching) to reduce soil temperature and maintain soil moisture.
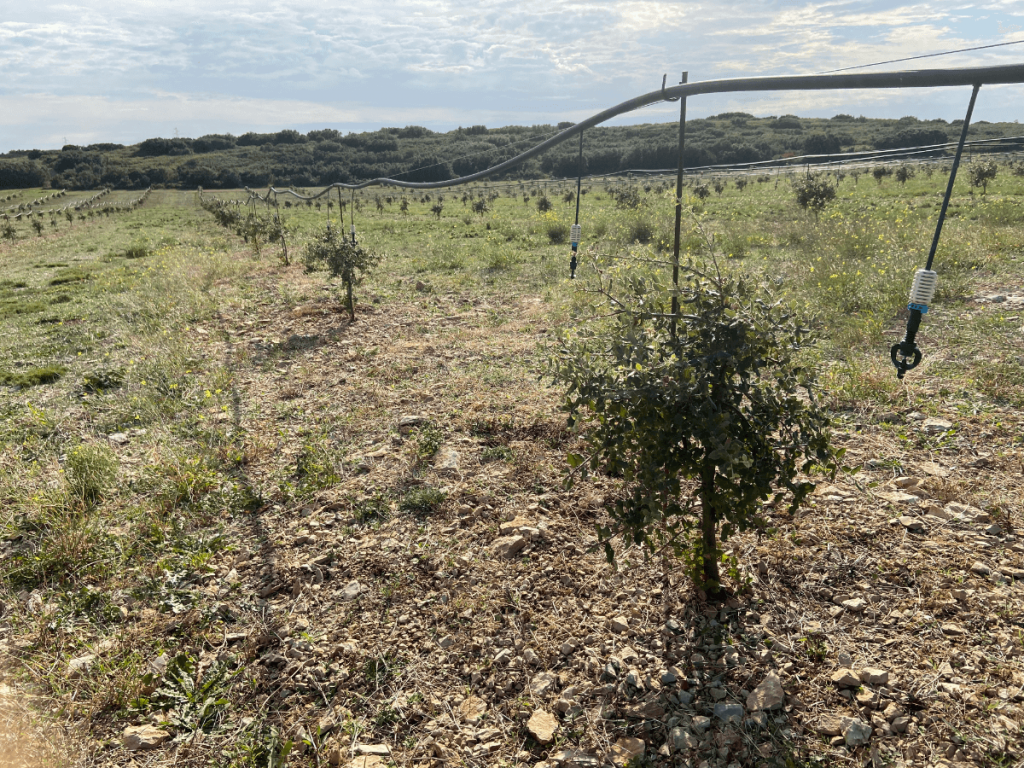
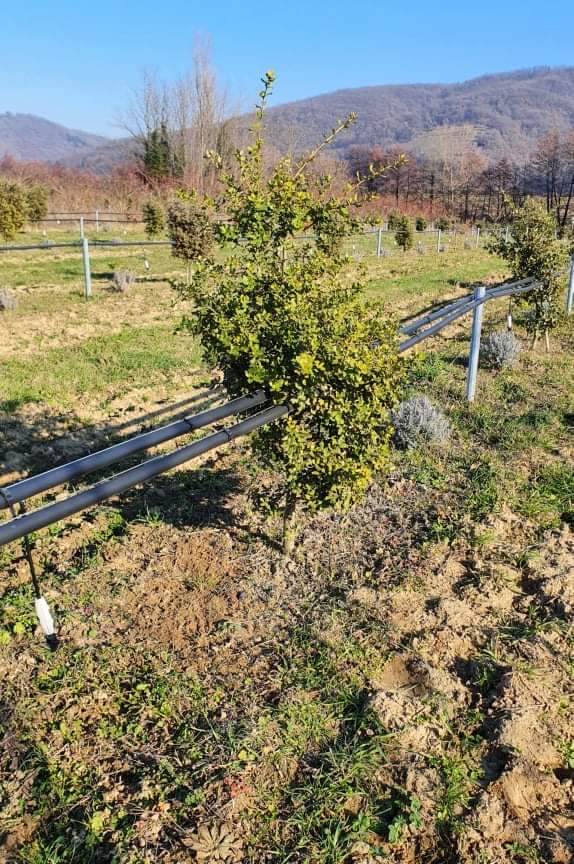





Are you interested? Visit here our truffle-growing training courses !
Subscribe to the newsletter to stay informed about our new training courses, our new products and our latest tips for growing your truffle farm!